History of the Israeli–Palestinian conflict | Arab-Israeli wars Timeline | History, Conflict, Causes and Summary
13th Oct 2023 Updates:
- Israeli army tells more than 1 million Palestinians living in the north of besieged enclave to move south within 24 hours ahead of expected ground offensive.
- UN says mass relocation “impossible”, could have devastating consequences. Hamas calls Israeli warning “fake propaganda”.
12th October 2023: Israel was warned by Egypt of potential violence three days before Hamas’ deadly cross-border raid, a US congressional panel chairman has said. Israeli PM Benjamin Netanyahu described the reports as “absolutely false”.
The scale and complexity of 7th October 2023 attacks by Hamas shocked leaders across the world, but they came after decades of a relentless and deadly conflict that has killed thousands of people, forced entire generations to grow up under occupation, or created constant anxiety of impending rocket fire or bombings.
More than 200 Israelis died in a surprise large-scale attack by the Palestinian militant group Hamas on October 7, 2023 the Israeli Army said, as Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu vowed to reduce the group’s Gaza hideouts to “rubble”.
Read more: Places In News Current Affairs MCQs
Palestinian militant group Hamas attack on Israel
Israeli media, citing rescue service officials, said at least 250 people were killed and 1,500 wounded, making Saturday’s (7 October 2023) surprise early morning attack by Hamas the deadliest attack in Israel in decades. At least 313 people in the Gaza Strip have been killed and at least 1,700 wounded in Israeli strikes, the Palestinian Health Ministry said.
Read more: International MCQs
The attack comes at a time of mounting tensions between Israel and the Palestinians, with the peace process effectively dead for years. Over the past year, Israel’s far-right government has ramped up settlement construction in the occupied West Bank, Israeli settler violence has displaced hundreds of Palestinians there and tensions have flared around a flashpoint Jerusalem holy site.
Indian PM Narendra Modi on Isreael Attack – Source: narendramodi /X
Israel Palestine Conflict has become a reason of International worry as people on both the sides have lost their lives due to it. The aspirants of various Government job exams can expect a few questions based on this event in their exams. Take a look at the questions below to cover this topic entirely.
What is Greater Israel?
What is Greater Israel? Why is the idea not acceptable to the Palestinians and Islamists?

The war between Israel and Palestine is more than a century old now and still is not under rest. Many International Organizations, historians and IR watchers are now under the impression of Israel’s bigger plans of Greater Israel in the picture. It has always been doubted that Israel has tried to fulfill its Zionist Plan for the Middle East and is slowly acceding territories to make it happen.
Read more: World Geography MCQs
- Greater Israel is an expression with a biblical and political meaning to it which has differed and evolved over time. It is called the Zionist Plan for the Middle East.
- The concept of a “Greater Israel”, according to the founding father of Zionism Theodore Herzl, is a Jewish State stretching “from the Brook of Egypt to the Euphrates.”
- Many historians and International Relations watchers state that this is the reason Israel is slowly and strategically grabbing more and more land from its neighbours, especially Palestine.
- While many other Zionists also say that Greater Israel included the land from the Nile in the West to the Euphrates in the East, comprising Palestine, Lebanon, Western Syria and Southern Turkey.
- However, it is also important to keep in mind that the design of Greater Israel may not strictly be a Zionist Project for the Middle East. Many experts and academics have stated recently that it is an integral part of US foreign policy aiming to extend US hegemony to the Middle East as well as fracturing and Balkanizing the Middle East.
- Such a policy being pursued by the US in the region goes along with the Yinon Plan. This plan is an Israeli strategy to ensure regional superiority. It is a continuation of an earlier ploy that Britain used in the Middle East.
- As per the Yinon Plan, Israel needs to reconfigure its geopolitical surroundings through Balkanisation of the surrounding Arab states turning them into smaller, weaker states.
1948–49: Israel’s War of Independence
In 1949, the newly created State of Israel signed a series of truces with Arab countries that had declared war on it. Under the 1949 agreements, the Gaza Strip was under Egypt’s control. In November 1947 the United Nations (UN) voted to partition the British mandate of Palestine into a Jewish state and an Arab state.
Q. What is the name of Israel’s air defense system?
- S 400 Defense System
- Iron Dome
- Air defense Dome
- ADGES
Ans. b
The clashes broke out almost immediately between Jews and Arabs in Palestine. As British troops prepared to withdraw from Palestine, conflict continued to escalate, with both Jewish and Arab forces committing belligerences. Among the most infamous events was the attack on the Arab village of DeirYassin on April 9, 1948. The news of a brutal massacre there by Irgun Zvai Leumi and the Stern Gang forces spread widely and inspired both panic and retaliation. Days later, Arab forces attacked a Jewish convoy headed for Hadassah Hospital, killing 78.
Read more: Defence Current Affairs MCQs
Q. Which country supported Israel in the development of Iron Dome?
- Iran
- Russia
- USA
- India
Ans. c
On the eve of the British forces’ May 15, 1948, withdrawal, Israel declared independence. The next day, Arab forces from Egypt, Transjordan (Jordan), Iraq, Syria, and Lebanon occupied the areas in southern and eastern Palestine not apportioned to the Jews by the UN partition of Palestine and then captured East Jerusalem, including the small Jewish quarter of the Old City.
Q. What was the old name of Jerusalem?
- Yerushalayim
- al-Quds
- Both a and b
- None of the above
Ans. c
Explanation: Jerusalem was known as Yerushalayim in Hebrew and as al-Quds in Arabic.
The stated purpose of the invasion was to restore law and order in light of British withdrawal, citing incidents such as that at Dayr Yasin, and a growing refugee crisis in neighbouring Arab countries. The Israelis, meanwhile, won control of the main road to Jerusalem through the Yehuda Mountains (“Hills of Judaea”) and successfully repulsed repeated Arab attacks. By early 1949 the Israelis had managed to occupy all of the Negev up to the former Egypt-Palestine frontier, except for the Gaza Strip.
Read more: Important Days and Events MCQs
Q. Which of the following statements is true regarding the Second Temple?
i) King Herod restructured the second Temple
ii) The retaining walls were added to the second temple in 37 BC
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. c
Explanation: In 37 BC King Herod restructured the second Temple and added retaining walls to it.
Between February and July 1949, as a result of separate armistice agreements between Israel and each of the Arab states, a temporary frontier was fixed between Israel and its neighbours. In Israel, the war is remembered as its War of Independence. In the Arab world, it came to be known as the Nakbah (or Nakba; “Catastrophe”) because of the large number of refugees and displaced persons resulting from the war.
Suez Crisis in 1956
In October 1956, a few months after the Egyptian president nationalized the Suez Canal waterway, cutting off Israel from shipping; Israel invaded the Sinai Peninsula and the Gaza Strip. In November that year, the United Nations called for Britain, France and Israel to withdraw their troops from Egypt.
Q. What according to Herzl were the boundaries of Greater Israel?
i) From the Brook of Egypt to the Euphrates
ii) South Lebanon up to Sidon and the Litani River
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. a
Tensions mounted again with the rise to power of Egyptian President Gamal Abdel Nasser, a staunch Pan-Arab nationalist. Nasser took a hostile stance toward Israel. In 1956 Nasser nationalized the Suez Canal, a vital waterway connecting Europe and Asia that was largely owned by French and British concerns. France and Britain responded by striking a deal with Israel—whose ships were barred from using the canal and whose southern port of Elat had been blockaded by Egypt—wherein Israel would invade Egypt; France and Britain would then intervene, ostensibly as peacemakers, and take control of the canal.
Read more: Science & Technology MCQs
Q. What was the great movement of the Jews from all over the world to Palestine called?
- Aliyahs
- Al Nakba
- Holocaust
- None of the above
Ans. a
In October 1956 Israel invaded Egypt’s Sinai Peninsula. In five days the Israeli army captured Gaza, Rafaḥ, and Al-ʿArīsh—taking thousands of prisoners—and occupied most of the peninsula east of the Suez Canal. The Israelis were then in a position to open sea communications through the Gulf of Aqaba. In December, after the joint Anglo-French intervention, a UN Emergency Force was stationed in the area, and Israeli forces withdrew in March 1957. Though Egyptian forces had been defeated on all fronts, the Suez Crisis, as it is sometimes known, was seen by Arabs as an Egyptian victory. Egypt dropped the blockade of Elat. A UN buffer force was placed in the Sinai Peninsula.
Q. What is the Palestine 194 Campaign?
i) This is Palestine’s initiative to include itself as a member of UNO
ii) It is the area to be given to Palestine
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. a
Read more: Reports And Indices Current Affairs MCQs
Six-Day War in 1967
In June 1967, during the Six-Day War, Israel gained control of the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula.
Arab and Israeli forces clashed for the third time June 5–10, 1967, in what came to be called the Six-Day War (or June War). In early 1967 Syria intensified its bombardment of Israeli villages from positions in the Golan Heights. When the Israeli Air Force shot down six Syrian MiG fighter jets in reprisal, Nasser mobilized his forces near the Sinai border, dismissing the UN force there, and he again sought to blockade Elat. In May 1967 Egypt signed a mutual defense pact with Jordan.
Q. Who is the initiator of Zionism?
- Jesus Christ
- Herzl
- Mohammad
- None of the above
Ans. b
Israel answered this apparent Arab rush to war by staging a sudden air assault, destroying Egypt’s air force on the ground. The Israeli victory on the ground was also overwhelming. Israeli units drove back Syrian forces from the Golan Heights, took control of the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt, and drove Jordanian forces from the West Bank. Importantly, the Israelis were left in sole control of Jerusalem.
Q. Who took over Palestine after the downfall of Ottoman Empire?
- America
- Britain
- Russia
- Iran
Ans. b
Yom Kippur War in 1973
On Yom Kippur in October 1973, invading forces from Egypt and Syria tried to persuade Israel to negotiate better terms for the Arab countries. Nearly 2,700 Israeli soldiers died in the 19-day war and thousands were injured out of a population of about 3 million at the time.
Read more: Most Important Current Affairs MCQs
The sporadic fighting that followed the Six-Day War again developed into full-scale war in 1973. On October 6, the Jewish holy day of Yom Kippur (thus, “Yom Kippur War”), Israel was caught off guard by Egyptian forces crossing the Suez Canal and by Syrian forces crossing into the Golan Heights. The Arab armies showed greater aggressiveness and fighting ability than in the previous wars, and the Israeli forces suffered heavy casualties. The Israeli army, however, reversed many of its early losses and pushed its way into Syrian territory and encircled the Egyptian Third Army by crossing the Suez Canal and establishing forces on its west bank. Still, it never regained the seemingly impenetrable fortifications along the Suez Canal that Egypt had destroyed in its initial successes.
Q. What is true about Israel in the statements listed below?
i) It is situated towards the east of Mediterranean Sea
ii) Jordan is the longest flowing river in Israel
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. c
Explanation: Israel is located at the eastern end of the Mediterranean Sea in Western Asia and Jordan is the largest flowing river of Israel.
The fighting, which lasted through the Islamic holy month of Ramadan, came to an end on October 26. Israel signed a formal cease-fire agreement with Egypt on November 11 and with Syria on May 31, 1974. A disengagement agreement between Israel and Egypt, signed on January 18, 1974, provided for Israeli withdrawal into the Sinai west of the Mitla and Gidi passes, while Egypt was to reduce the size of its forces on the east bank of the canal. A UN peacekeeping force was established between the two armies. This agreement was supplemented by another, signed on September 4, 1975.
Read more: Current Affairs Monthly MCQs
Q. Choose the correct statement about Abraham from below:
i) Abraham believed that there is only one God who is the creator of the Universe
ii) His son’s name was Isaac who he tried to sacrifice for God
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. c
On March 26, 1979, Egypt and Israel signed a peace treaty at the White House which led to Israel’s complete withdrawal from the Sinai Peninsula. The two countries agreed on the framework of an agreement to allow for self-rule for Palestinians living in occupied territories. Three years later, President Reagan expressed his support for their full autonomy with some Jordanian supervision, but Israel rejected the plan.
Q. Who proclaimed Palestine to be independent?
- UNO
- PLO
- USA
- None of the above
Ans. b
Q. Who is Israel named after?
- Abraham
- Moses
- Jacob
- Yitshak
Ans. c
Lebanon War in 1982
On June 5, 1982, less than six weeks after Israel’s complete withdrawal from the Sinai, increased tensions between Israelis and Palestinians resulted in the Israeli bombing of Beirut and southern Lebanon, where the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) had a number of strongholds. The following day Israel invaded Lebanon, and by June 14 its land forces reached as far as the outskirts of Beirut, which was encircled, but the Israeli government agreed to halt its advance and begin negotiations with the PLO. After much delay and massive Israeli shelling of west Beirut, the PLO evacuated the city under the supervision of a multinational force. Eventually, Israeli troops withdrew from west Beirut, and the Israeli army had withdrawn entirely from Lebanon by June 1985.
In December 1987, Palestinians living in the West Bank and Gaza started the First Intifada against Israel. Muslim Brotherhood members founded Hamas.
Q. Where is the name Jew derived from?
- Jacob
- Yehuda
- Abraham
- Yosef
Ans. b
Q. Where is the Sinai Peninsula located?
i) It is located between Red Sea and the Mediterranean Sea
ii) It is the territory of Israel
iii) It is the only part of Egypt in Asia
- Only i
- i and ii
- ii and iii
- i and iii
Ans. d
The Oslo peace accords
In 1993, Mr. Arafat signed the Oslo accords with Israel, and committed to negotiating an end to the conflict based on a two-state solution. Hamas, which opposed the deal, launched a series of suicide bombings in Israel.
In September 2000, a few months after negotiations between Israel and Palestine reached an impasse at Camp David; a Second Intifada began, with Palestinian youth throwing stones at Israeli police. Support for Hamas continued to grow within Palestine because of its readiness to fight Israel.
In 1997, two suicide bomb attacks killed 27 people, and Israel’s Prime Minister, Shimon Peres, said he would wage an incessant war against Hamas.
In September 2005, Israeli troops pulled out of Gaza, but Israel came under criticism for restricting the movement of Palestinians coming in and out of the strip.
In January 2006, about a year after the death of the Palestinian leader Yasir Arafat, the co-founder of the paramilitary organization Fatah, Hamas won the Palestinian parliamentary election. One year later, Hamas seized control of Gaza, routing the Fatah forces.
Read more: Must Read Books for Competitive Exams
Q. Which of the statements stands true for Jerusalem?
i) Jesus was said to be born in Jerusalem
ii) King Herod restructured the second Temple and added retaining walls to it
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. b
Q. Muslim Quarter in Jerusalem houses al Aqsa Mosque. Where is it situated?
- On plateau of Haram al Sharif
- On the West Bank
- On Dome Rock
- On the bank of Jordan
Ans. a
Second Lebanon War 2006
In July 2006 Hezbollah launched an operation against Israel in an attempt to pressure the country into releasing Lebanese prisoners, killing a number of Israeli soldiers in the process and capturing two. Israel launched an offensive into southern Lebanon to recover the captured soldiers. The war lasted 34 days but left more than one thousand Lebanese dead and about one million others displaced. Several Arab leaders criticized Hezbollah for inciting the conflict. Nevertheless, Hezbollah’s ability to fight the Israel Defense Forces to a standstill won it praise throughout much of the Arab world.
In response to rocket fire from Gaza, Israel launched an attack on Hamas targets in December 2008 that killed 200 Palestinians. Shortly after, they opened a ground war against Hamas. In total, 1,200 Palestinians and 13 Israelis were killed.
In January 2009, Israel and Palestinian groups declared unilateral cease-fires, then Israel withdrew from Gaza, and redeployed to the Strip’s perimeter.
In November 2012, Israel killed Ahmed al-Jabari, Hamas’s military chief, setting off more than a week of an exchange of fire in which more than 150 Palestinians and at least six Israelis are killed.
In 2018, at least 170 Palestinians were killed as Israel responded to protests along the barrier fence that separates Gaza and Israel.
In 2014, Hamas kidnapped and killed three Israeli teenagers, prompting attacks from Israel, and rocket launches from Gaza, in a conflict that killed more than 1,881 Palestinians and more than 60 Israelis.
In May 2021, the Israeli police raided Al-Aqsa Mosque in Jerusalem, the third-holiest site in Islam, which set off an 11-day war between Israel and Hamas that killed more than 200 Palestinians and more than 10 Israelis.
After a spate of terrorist attacks in Israeli cities in 2022, Israeli forces killed at least 166 Palestinians in the Israeli-occupied West Bank.
United Nations on Greater Israel
As stated in a UN report in 2017, ‘Israel is currently proceeding with the plan to annex large chunks of Palestinian territory while keeping the Palestinian inhabitants in conditions of severe deprivation and isolation’.
As per the research, Israel is proceeding with the plan to annex large chunks of Palestinian territory “while keeping the Palestinian inhabitants in conditions of severe deprivation and isolation.
The idea of Greater Israel has sparked aggression all over the globe and Muslim community is seen to have turned violent due to that. Very recently the Israeli troopers raided the Al- Aqsa Mosque and Muslims all over the Globe protested on streets and the social media.
The protests were held in Germany, London, Australia and India as well.
What is Hamas and its role in Israel- Palestine Conflict?
- Hamas is a Palestinian Sunni-Islamic fundamentalist, militant group.
- After the airstrikes, Hamas also pressed on the idea of launching rockets from civilian areas in Gaza toward civilian areas in Israel.
- The death toll in Gaza has risen overnight to 119 Palestinians, including 31 children and 19 women as per Gaza’s health ministry.
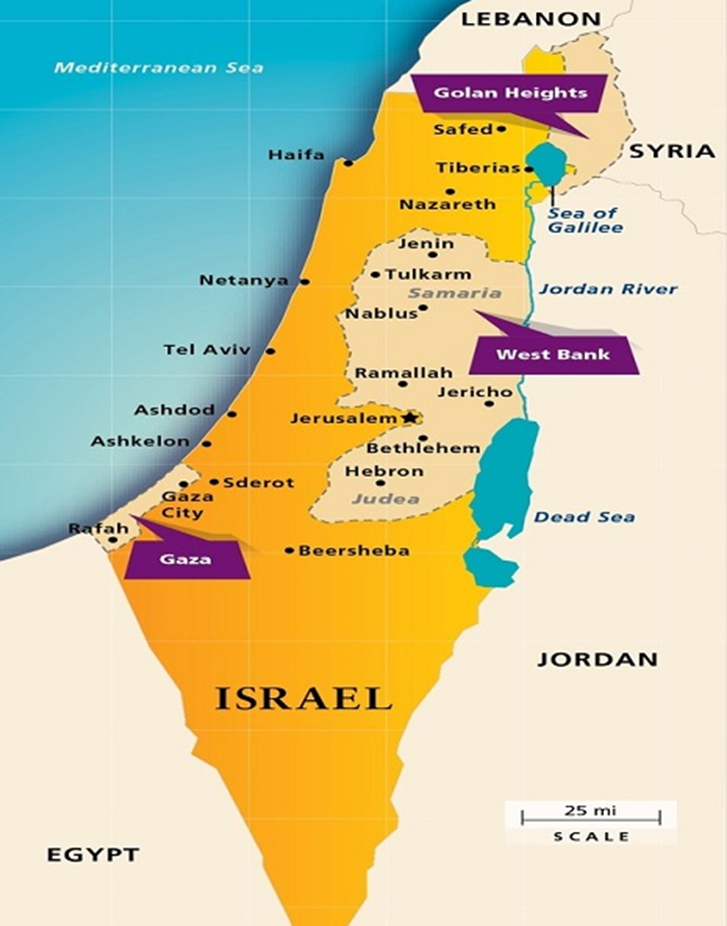
Palestine is divided into Gaza strip and West Bank (situated west of Dead Sea). Take a look at the Map below showing Israel- Palestine in biblical times and current times.
When and how was Hamas formed?
The protest initially began in Jerusalem. The tensions escalated because in the Gaza strip where Hamas has been prevalent attacked various parts of the country. In the year 1989 Palestine Liberation Organization declared the area to be free and under the Palestinians. Until 1948, Palestine typically referred to the geographic region located between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River. Palestinians understood that they needed a political solution when Israel gained power. Fatah, an organization was formed to initiate a political solution to the issue. Fatah was formed in 1950, which is now led by Mohd Abbas. Fatah was liberal but in 1987, a radical organization Hamas came into being against Fatah. It promoted Muslim brotherhood.
- There was division observed between Palestinian movement then itself. It was in the year 1987, when the First Intifada broke out. It was due to Palestinian anger over occupation of Gaza and the West Bank by Israel. Palestinian militia groups revolted, and hundreds of people were killed.
- Then, a subsequent peace process, called the Oslo Peace Accord, was initiated during the early 1990s to end the ongoing violence.
- Oslo I did the work of creating a timetable for a Middle East peace process along with a plan for an interim Palestinian government in parts of Gaza and the West Bank.
- An agreement was signed in 1993 in the presence of the Israeli Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin and Palestinian leader Yasser Arafat. Palestinian Legislative Council was formed and two elections have been carried out since then.
In the 2006 elections 132 seats were fought for. Hamas gained political power in Gaza strip and West Bank areas. Hamas wanted to win Israel and won 73 seats. Fatah won only 45 seats. In 2021 elections were announced again. So after the beginning of firing of rockets leading to a conflict many people wanted to know the real intentions of Hamas.
Q. Choose the correct statement about Israel Palestinian Conflict:
i) The Isaraeli-Palestinian conflict is an ongoing struggle since mid-20th century
ii) Between 1882 to 1948, the Jews from around the world gathered in Palestine
- Only i
- Only ii
- Both i and ii
- None of the above
Ans. C