Main Concepts and Types of Business Environment: There are mainly two types of business environment—internal and external. A business has absolute control in the internal environment, whereas it has no control on the external environment. It is therefore, required by business, to modify their internal environment on the basis of pressures from external.
Types of Business Environment
Mainly two types of business environment: Internal and External.
Internal Environment
This has received considerable attention by various business firms. This includes the owner of the business, the shareholders, the managing director, the non-managers, employees, the customers, the infrastructure of the business organization, and the culture of the organization.
It includes 5 Ms:
1. Men – Human Resources
2. Material – Raw Inputs
3. Money – Financial Assets
4. Machine – Physical Assets
5. Methods – Technology
Management is counted as another ‘M’, though it may be reflected through ‘Men’. Then there are ‘Miscellaneous Factors’, such as R and D, Brand Equity, Value System, Competitive Advantage, etc.
Usually, these factors are within the control of the business. Business can make changes in these factors according to the change in the functioning of enterprise.
The internal analysis of strengths and weaknesses focuses on internal factors that give an organization certain advantages and disadvantages in meeting the needs of its target market thereby gaining the competitive edge over the competitors.
Some examples of internal factors are:
1. Financial resources like funding, investment opportunities and sources of income.
2. Physical resources like company’s location, equipment, and facilities.
3. Human resources like employees, target audiences, and volunteers.
External Environment
This kind of environment of an organization comprises of all entities that exists outside its boundaries, but have significant influence over its growth and survival. An organization has little or no control over its external environment but needs to constantly monitor and adapt to these external changes. A proactive or reactive response leads to significantly different outcomes. Economic, sociocultural, political, legal, technical, and environmental considerations are different examples of external environment. External environment may be identified more with systematic risk.
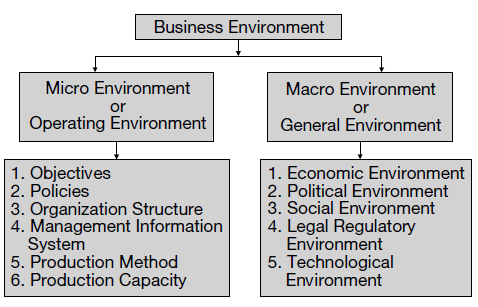
Micro and Macro Environment
Another classification of business environment divides them into the following types.
1. Micro/Operating Environment
2. Macro/General Environment
Micro Environment
The micro environment is also known as the task environment or operating environment because the micro environmental forces—though external factors—still have a direct bearing on the operations of the firm. The micro environment consists of the factors in the company’s immediate environment that affects the performance and working of the company. The micro environmental factors are more intimately linked with the company than the macro factors. The micro forces need not necessarily affect all the firms in a particular industry in the similar ways.
Micro environmental or operating environmental factors, as a part of internal environment, also impact the business strategy.
Macro Environment
Macro environment is also known as general environment or remote environment. Macro environmental factors are generally more uncontrollable than micro environmental factors. These factors keep changing. The success of an organization depends upon its adaptability to the environment. This environment has a bearing on the strategies adopted by the firms and any changes in the areas of the macro environment are likely to have a far-reaching impact on their operations.
The macro environment is primarily concerned with major issues and upcoming changes in the environment.
The acronym for the macro analysis is also called “STEEP”.
The five areas of interest are:
1. Socio-Cultural and Demographics
2. Technology
3. Economic Conditions
4. Ecology and Physical Environment
5. Political and Legal
Business Environment of Air India
| Social | Earlier, being the national flagship airline, Air India had social value. It catered to both domestic and international flights, and attended to all – be it individuals, business class, tourists, and so on. |
| Technical | Air India always uses state-of-the-art technology for safety, convenience, and efficient services. Air India Express becomes India’s first airline to introduce robotic technology to disinfect and clean aircraft interiors for its Boeing 737-800 aircrafts. |
| Economic | The prime challenge for Air India is that it is not making profit due to high fuel costs and bureaucratic controls. |
| Ecological | Air pollution such as release of carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide cause issues such as asthma; chronic bronchitis; emphysema; sleeplessness (insomnia) |
| Political | Air India is the flag carrier airline of India. It is now owned by Talace Pvt. Ltd, a Special-Purpose Vehicle (SPV) of Tata Sons. There has always been political resistance for its privatization. |
There are words such as PEST (Political, Economic, Social and Technological) and PESTLE (Political, Economic, Sociocultural, Technological, Legal and Environmental) to describe the components of business environment.
Read more: Business Environment and International Business : The Basics of Business Environment