Business Environment: Economic System -The Commerce subject detailed notes with practice tests are very useful for Assistant Professor / UGC NET / JRF and other competitive exams preparation. The economy is basically about production and consumption of goods and services. There are four major factors of production: land, labour, capital and entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship means to make profits by combining land, labour and capital in an optimum manner.
Parts of an Economic System
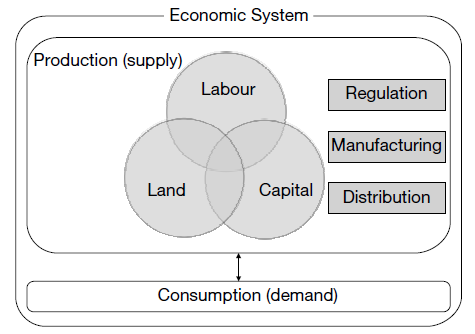
The concept of ‘circular flow of income’ also helps us to understand how our economy functions.
There are basically two types of economic systems – free market systems and planned systems.
The three basic questions in any economic system are as follows:
1. What will be produced?
2. How will it be produced?
3. For whom will it be produced?
The different goals of an economic system are:
1. Economic Freedom
2. Economic Efficiency
3. Economic Equity (or Fairness)
4. Economic Growth
5. Economic Security
6. Economic Stability
7. Environmental Sustainability
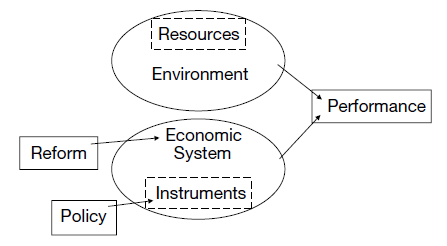
The system is ultimately to be translated into plans, policies and business environment to ensure the welfare of the people. The following formal categorization of economic systems will help us to find answers to these issues.
Capitalism
In capitalism, the state has no control over the factors of production. Here, the individuals and firms own economic resources and industry. They ‘compete’ for resources so as to increase capital (or wealth) and develop personal success. Thus, individualism and competition are basic to capitalism.
The potential success of each individual is decided on merit and is also valued. People are encouraged to direct their talents in a way that benefits themselves, such as by starting a business or entering a highly profitable profession.
Competition decides the checks and balances in capitalist society. Individuals who own capital compete with others to provide goods and services to the marketplace; those who produce and effectively market goods in demand, at a price that people want to pay, are likely to succeed.
Similarly, businesses that treat their workers well and pay good wages are most likely to attract good employees, which is more likely to mean success for the business. Those who offer inferior service or fail to attract good workers will eventually fail and leave the marketplace.
Low taxes are generally a goal of capitalistic governments. In addition, government funding for public services, like social service benefits, are generally kept to a minimum.
Types of Capitalism
When discussed theoretically, capitalism has several unique defining characteristics. A market economy requires three dimensions—free choice, free enterprise and price flexibility.
In practice, capitalism can be classified into the following types:
1. Free-market Capitalism: This capitalism leaves all aspects of a society to be governed by the market, with little or no intervention from the government. Here, the role of the government is limited to protect the lives and property of the citizens.
In 18th century, Laissez-faire opposed any government intervention in business affairs. Laissez-faire is a French term that translates as “leave alone” (literally, “let you do”). It means that lesser the government involvement in the economy, the better off the business will be. By extension, it may apply to the whole society. Laissez-faire economics is a part of free market capitalism. Canada and USA are main examples.
2. Corporate Capitalism: In this type of economy, large, bureaucratic corporations dominate the economy. This allows for long-term planning and efficiency, but for less innovation. Large corporations enjoy large influence over the government. It helps in legislation that is designed to protect the interests of those corporate houses.
3. Social-democratic or Social Market Economy: This economic system tries to balance the benefits of a free-market system with a strong social support structure. The most industries are privately owned. It is the duty of government to ensure that competition is fair (antitrust or antimonopoly) and rate of unemployment is low. The social welfare is provided to the needy.
4. State–lead Capitalism: The means of production are owned by government, but run in an entrepreneurial “capitalistic” way – that means profit. The term describes an economy where the government steps in to protect the interests of firms.
The success of capitalism depends upon markets. A company needs to adopt its strategy as per market conditions. The markets can also be divided into three types:
1. Developed Markets: The infrastructure is highly developed. These are established and efficient consumer markets. The middle class is the main consumer, they consume any desired product.
2. Emerging Market: The emerging markets are trying their level best to achieve the status of developed markets. They are so due to industrialization, urbanization of developing nations such as China, Brazil, India, Indonesia, etc. The demand is increasing for global products. They are bigger than developed markets.
3. Traditional Markets: They are the largest of all. They lack good infrastructure and physical amenities; they are basically rural.
The government role in a capitalist or market economy depends upon the following essentials:
1. Framing antitrust (antimonopoly) or similar act, such as Competition Commission of India
2. Framing of Property Rights
3. Stable fiscal and monetary system
4. Political stability for smooth conductance of business
Market failure: This occurs when individuals acting in rational self-interest produce a less than optimal or economically inefficient outcome.
Socialism
Socialism mainly relies upon the governmental planning, rather than the marketplace, to distribute our resources. While individuals in a socialist nation do their own businesses or they offer professional services directly to consumers, they are usually taxed heavily on their profits. Public services are typically numerous and funded by taxpayer money. Citizens are expected to work. The government provides them education, healthcare, and public transportation services for free or at a very low cost. Socialist countries also often have extensive social welfare systems to aid the unemployed, disabled, and elderly.
Business owners usually pay high taxes, they usually comply with strict labour laws designed to protect workers against exploitation. These laws may be factory act, women safety act, etc. The medical care is usually provided through national health care systems.
Types of Socialism
There are a wide range of socialist political philosophies, including Marxism and reformism.
1. Marxism: This originates from the works of Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels. It argues that socialism is the mid-point between capitalism and communism, with the means of production controlled by the working class but with the state guiding the economy on the workers’ behalf.
2. Reformism: It is also called the social democracy. It usually focuses on changing capitalist societies, but from within, through political process and government reforms.
There are number of different economic theories of socialism:
1. Market Socialism: This mechanism involves running public or cooperative companies within the free market. Rather than depending on taxes, the government takes all profits and redistributes them by paying employees, funding public institutions, and offering social services.
2. Socialism in a Planned Economy: The government owns the means of production, and plans out what will be produced, how much will be made, and the price it will sell for.
3. Self–managed Economies: They depend on the collective actions of specific groups to make decisions. For example, a self-managed company may be owned by its workers, who collectively decide the direction of the business.
4. State Socialism or State–directed Economies: They have industries that are owned cooperatively, but which operate with some planning or direction from the government.
Communism
Many people confuse socialism with communism. As per definition, everything is owned communally or by everyone in communism. There is spirit of ‘collectivism’ in communism. Ideally, there is no government or class division, and no money; each person contributes to society as per one’s best ability and takes away from society only what is required by him or her. The social decisions benefit all members of society. They are not meant for any individual.
Historically, “communist nations” practice some form of socialism, usually run by one political party. The state typically owns all forms of production and practiced very strict central planning. The government decides how resources are to be used. Many of us argue that most ‘communist’ governments actually behave very differently.
In a centrally planned economy, nation’s land, factories and other economic resources are owned by government. Government decides who produces what and also about prices of product, labour and capital. The best example is that of the Soviet Union (USSR). Karl Marx popularised the idea of central economic planning in the nineteenth century.
In the late 1980s and later, many nations including the main ideologist USSR started dismantling communism. The policies of glasnost (openness) and perestroika (economic reforms) started. East Germany merged with West Germany in 1990 as a result of such trend. USSR got disintegrated into fifteen nations. Many East European nations such as Poland, Romania and Hungary also shunned communist path. Now, only North Korea and Cuba are communist nations. China is a communist nation but with many capitalist measures.
The main reasons for the decline of socialism are as follows.
1. USSR declined as an economy, though it showed good growth during economic crisis of 1930s.
2. Communism added little value to its practicing economies.
3. The main focus was on defense, aerospace, and nuclear power, etc. The consumer industries were neglected. Even today, Russia has very less consumer brands.
The economy can be described in the following manner also.
In a totalitarian system, leaders govern without the support of people, and do not tolerate opposing viewpoints. In a theocracy, country’s religious leaders are also its political leaders.
Mixed Economy
In such economy, resources such as land, labour, capital are equally split between private and government sector. Here, government has much less resources in comparison to communism. The government investment goes into sectors that are held important by government such as steel, power, oil, defence, to name a few while others are thrown open for private sector. Even within mixed economies, focus shifted on to LPG – Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization.
Very few societies are purely capitalist or purely socialist, although most are more strongly one than the other. USA, for example, is considered to be a capitalist society, but the Social Security system, which provides support for people who are unable to work, is socialistic. Sweden is considered by some people to be a socialist country because of its high tax rate and large welfare system, but the majority of industry in the nation is in private hands, which is capitalistic.
Some Further Analysis
1. Communism and socialism are basically the umbrella terms referring to left-wing schools of economic thought that oppose capitalism. The criticisms of both capitalism and socialism start from ideologies. Capitalists believe in ‘individualism’ while socialism or communism believes in ‘collectivism’.
2. Criticism for the capitalism arises from the fact that the marketplace can be unstable. It poses real dangers to the vulnerable sections of society. This may give rise to issues such as unemployment and social insecurities. On the other hand, business owners can establish a wealthy class which, in turn, can suppress the freedom of others. A purely capitalist society may exploit labour class.
3. We need to differentiate between socialism and capitalism. Communism follows the teachings of Marx and Lenin that believes that a violent revolution is a must to have a control over resources and to eliminate political opposition. Socialism believes in none of these. In fact, every government undertakes some welfare measures. Communists claim to be socialists but socialists are not necessarily communists.
4. Excessive reliance on socialism results in heavy taxation to provide equal social services for all citizens. There is discouragement for business owners from innovation and excellence, as business owner won’t be suitably rewarded for his efforts. Choices are little for consumer. Families may slip into poverty.
Business Environment: Economic Environment
Main Concepts and Types of Business Environment
Business Environment and International Business : The Basics of Business Environment